“Ethernet库”的版本间的差异
| (未显示1个用户的1个中间版本) | |||
| 第7行: | 第7行: | ||
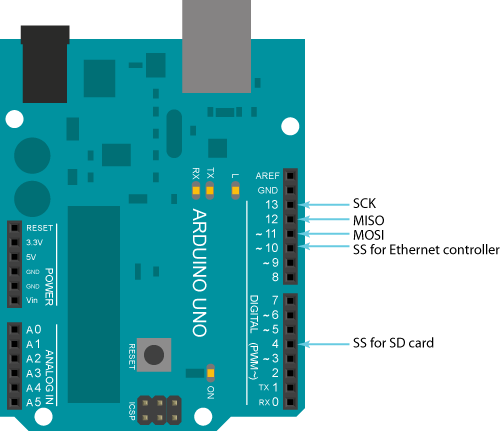
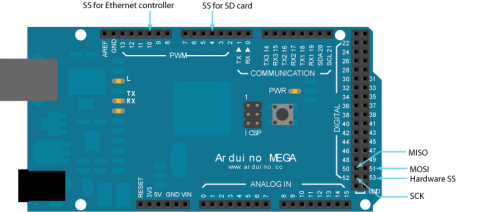
Arduino communicates with the shield using the SPI bus. This is on digital pins 11, 12, and 13 on the Uno and pins 50, 51, and 52 on the Mega. On both boards, pin 10 is used as SS. On the Mega, the hardware SS pin, 53, is not used to select the W5100, but it must be kept as an output or the SPI interface won't work. | Arduino communicates with the shield using the SPI bus. This is on digital pins 11, 12, and 13 on the Uno and pins 50, 51, and 52 on the Mega. On both boards, pin 10 is used as SS. On the Mega, the hardware SS pin, 53, is not used to select the W5100, but it must be kept as an output or the SPI interface won't work. | ||
| − | + | <br><br><br> | |
| + | [[File:arduino_uno_ethernet_pins.png|500px]] | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | [[File:arduino_mega_ethernet_pins.png|500px]] | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<font color="orange" size="+2">'''Examples'''</font><br> | <font color="orange" size="+2">'''Examples'''</font><br> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | :-[[ ChatServer]] : set up a simple chat server. | ||
| + | :-[[ WebClient]] : make a HTTP request. | ||
| − | + | :-[[ WebClientRepeating]] : Make repeated HTTP requests. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ WebServer]] : host a simple HTML page that displays analog sensor values. |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ BarometricPressureWebServer]] : outputs the values from a barometric pressure sensor as a web page. |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ UDPSendReceiveString]] : Send and receive text strings via UDP. |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ UdpNtpClient]] : Query a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server using UDP. |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ DnsWebClient]] : DNS and DHCP-based Web client. |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ DhcpChatServer]] : A simple DHCP Chat Server |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[ DhcpAddressPrinter]] : Get an IP address via DHCP and print it out |
| − | + | :-[[ TelnetClient]] : A simple Telnet client | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | :-[[ TelnetClient]]: A simple Telnet client | + | |
|width="10%" valign="top" align="left"| | |width="10%" valign="top" align="left"| | ||
| 第47行: | 第43行: | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | <font color="orange" size="+2">''' | + | <font color="orange" size="+2">'''Ethernet class'''</font><br><br> |
| − | '''The | + | '''The Ethernet class initializes the ethernet library and network settings. ''' |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Ethernet.begin()| begin()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Ethernet.localIP()| localIP()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Ethernet.maintain()| maintain()]] |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | <font color="orange" size="+2">''' | + | <font color="orange" size="+2">'''IPAddress class'''</font><br><br> |
| − | '''The | + | '''The IPAddress class works with local and remote IP addressing. ''' |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Ethernet.IPAddress()()| IPAddress()]] |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <font color="orange" size="+2">'''Server class'''</font><br><br> | ||
| − | + | '''The Server class creates servers which can send data to and receive data from connected clients (programs running on other computers or devices). ''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | :-[[Server.Server()| Server()]] | |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Server.EthernetServer()| EthernetServer()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Server.begin()| begin()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Server.available()| available()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Server.write()| write()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Server.print()| print]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Server.println()| println()]] |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | <font color="orange" size="+2">'''Client class'''</font><br><br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <font color="orange" size="+2">''' | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''The client class creates clients that can connect to servers and send and receive data. ''' | |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.Client()| Client()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.EthernetClient()| EthernetClient()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.if (EthernetClient)| if (EthernetClient)]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.connected()| connected()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.connect()| connect()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.write()| write]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.print()| print]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.println()| println()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.available()| available()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.read()| read()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[Client.flush()| flush()]] |
| + | :-[[Client.stop()| stop()]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <font color="orange" size="+2">''' | + | <font color="orange" size="+2">'''EthernetUDP class'''</font><br><br> |
| − | '''The | + | '''The EthernetUDP class enables UDP message to be sent and received. ''' |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.begin()| begin()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.read()| read()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.write()| write()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.beginPacket()| beginPacket()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.endPacket()| endPacket()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.parsePacket()| parsePacket()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.available()| available()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.stop()| stop()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.remoteIP()| remoteIP()]] |
| − | :-[[ | + | :-[[EthernetUDP.remotePort()| remotePort()]] |
|width="10%" valign="top" align="left"| | |width="10%" valign="top" align="left"| | ||
2015年7月23日 (四) 23:08的最后版本
|
With the Arduino Ethernet Shield, this library allows an Arduino board to connect to the internet. It can serve as either a server accepting incoming connections or a client making outgoing ones. The library supports up to four concurrent connection (incoming or outgoing or a combination). Arduino communicates with the shield using the SPI bus. This is on digital pins 11, 12, and 13 on the Uno and pins 50, 51, and 52 on the Mega. On both boards, pin 10 is used as SS. On the Mega, the hardware SS pin, 53, is not used to select the W5100, but it must be kept as an output or the SPI interface won't work.
Examples
|
Ethernet class The Ethernet class initializes the ethernet library and network settings.
The IPAddress class works with local and remote IP addressing.
The Server class creates servers which can send data to and receive data from connected clients (programs running on other computers or devices).
The client class creates clients that can connect to servers and send and receive data.
The EthernetUDP class enables UDP message to be sent and received.
|
更多建议和问题欢迎反馈至 YFRobot论坛